What is Diabetes
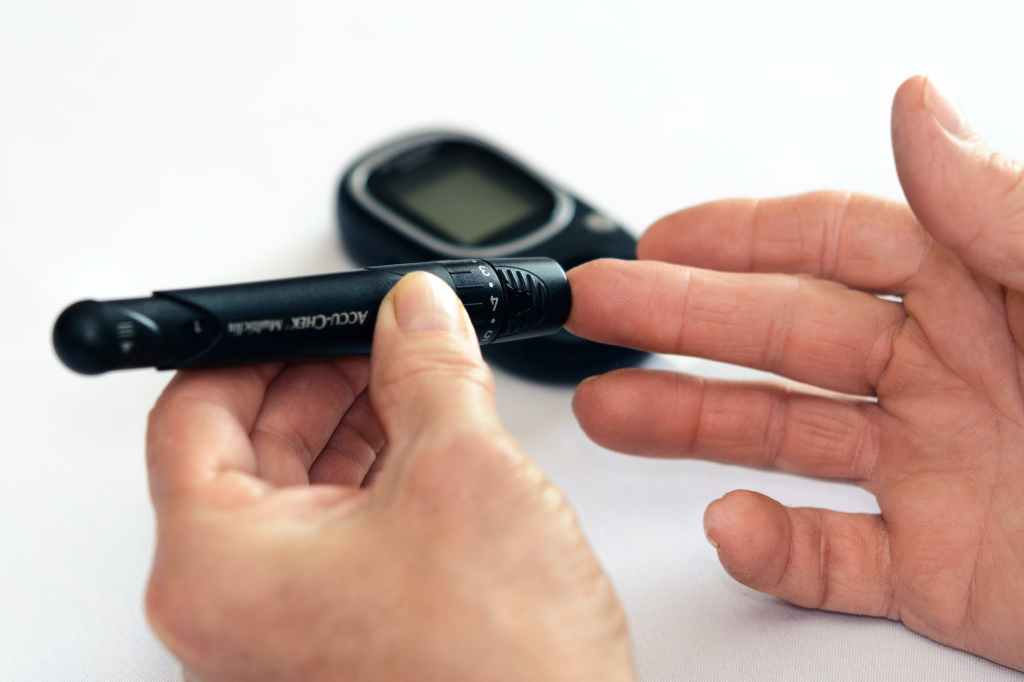
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels effectively, leading to various health complications. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the causes of diabetes, the telltale signs to watch out for, and the different types of diabetes. Additionally, we will provide valuable insights and real-world information to help you understand this condition better.
1. How Diabetes is Caused
Diabetes develops when there is a disruption in the body’s ability to manage glucose, the primary source of energy. This disruption can be attributed to various factors:
a. Genetics:
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of diabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes, you may be at a higher risk.
b. Lifestyle Factors:
Sedentary lifestyles and poor dietary choices can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Consuming excessive sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can lead to insulin resistance.
c. Autoimmune Response:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
d. Hormonal Changes:
Certain conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hormonal imbalances can increase the risk of diabetes.
2. Signs of Diabetes
Recognizing the signs of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Common symptoms include:
a. Excessive Thirst and Urination:
Frequent urination and an unquenchable thirst are classic signs of diabetes, as high blood sugar levels lead to increased fluid intake and urination.
b. Fatigue:
High or low blood sugar levels can cause fatigue, as the body’s cells are not receiving the energy they need.
c. Unexplained Weight Changes:
Sudden weight loss in type 1 diabetes and unexplained weight gain in type 2 can be indicative of the condition.
d. Blurry Vision:
High blood sugar levels can affect the eyes and lead to blurred vision.
e. Slow Wound Healing:
Diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds, making even minor injuries more problematic.
f. Numbness and Tingling:
Peripheral neuropathy is a common complication, causing numbness and tingling in the extremities.
3. Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is not a one-size-fits-all condition. There are primarily three types:
a. Type 1 Diabetes:
This is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy.
b. Type 2 Diabetes:
The most common form of diabetes, type 2, is often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise. It’s characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin production.
c. Gestational Diabetes:
Occurring during pregnancy, gestational diabetes can affect both the mother and the unborn baby. It usually resolves after childbirth, but it increases the risk of type 2 diabetes later in life.
4. Real Information about Diabetes
It’s essential to understand that diabetes is a manageable condition. With proper medical care, lifestyle changes, and support, people with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Real-world insights include:
a. Diabetes Management: Individuals with diabetes often manage their condition through a combination of insulin or other medications, diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring.
b. Dietary Guidelines: A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is vital for diabetes management. Monitoring carbohydrate intake is also crucial.
c. Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and can aid in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
d. Monitoring: Frequent blood sugar monitoring and periodic HbA1c tests are essential for tracking progress and making necessary adjustments.
e. Complications: Long-term uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, and eye issues. Regular medical check-ups are necessary.
Diabetes is a complex condition with various causes, signs, and types. Understanding its intricacies and seeking early diagnosis is pivotal for effective management. Whether you or a loved one is affected by diabetes, the right information, lifestyle choices, and medical guidance can help in leading a healthier and more fulfilling life. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with diabetes can minimize the risks of complications and enjoy a better quality of life.